
Navigating Mobile Fragmentation
10 Essential Strategies for Software Testers


Introduction
Mobile fragmentation is a significant challenge in the mobile software development landscape. It refers to the diversity and variety of hardware and software configurations found in the mobile device market. This fragmentation arises from differences in operating systems, hardware specifications, screen sizes, and manufacturer customizations. For developers, testers, and businesses, this presents a multitude of challenges, from ensuring compatibility and performance to maintaining a consistent user experience. This article explores the intricacies of mobile device fragmentation, its implications, and the strategies to effectively manage it.

The Scope of Mobile Device Fragmentation
Operating System Variations
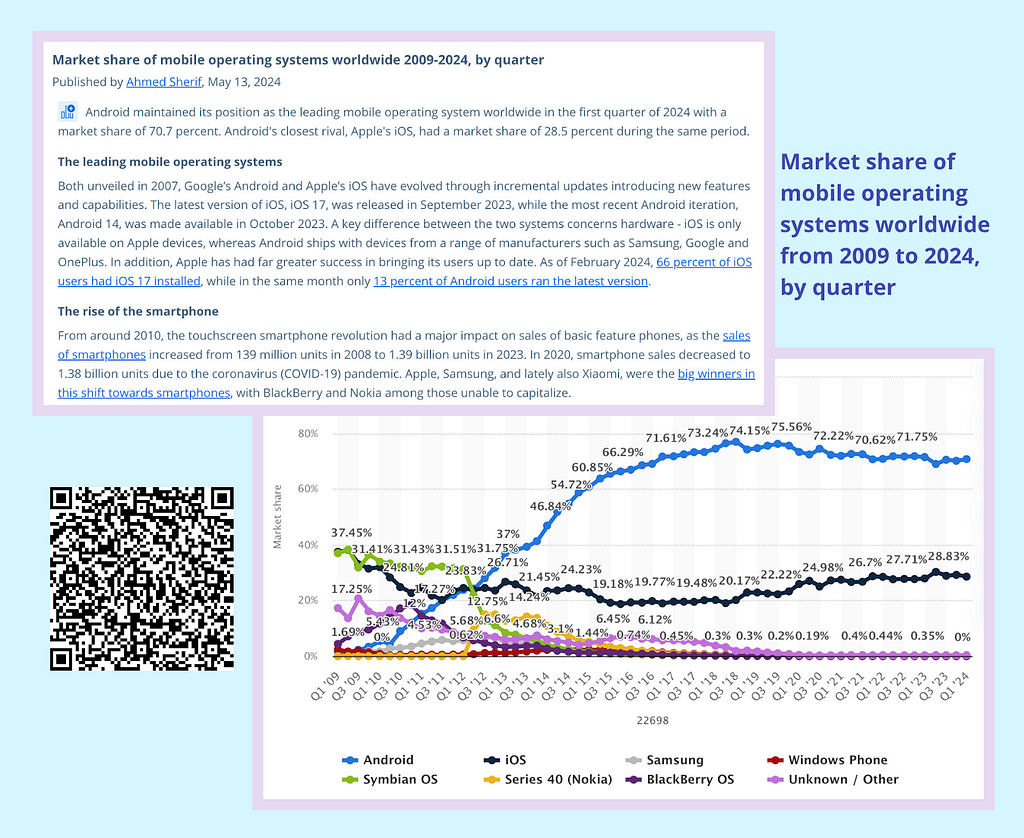
The most prominent aspect of fragmentation is the diversity of operating systems, particularly in the Android ecosystem. Unlike iOS, where Apple controls both the hardware and software ecosystem, Android devices are manufactured by a multitude of companies, each with the freedom to modify the Android Open Source Project (AOSP) to their liking. This results in numerous versions and customizations of Android. Consequently, developers must consider a range of OS versions, each with different APIs and security features, when creating applications.
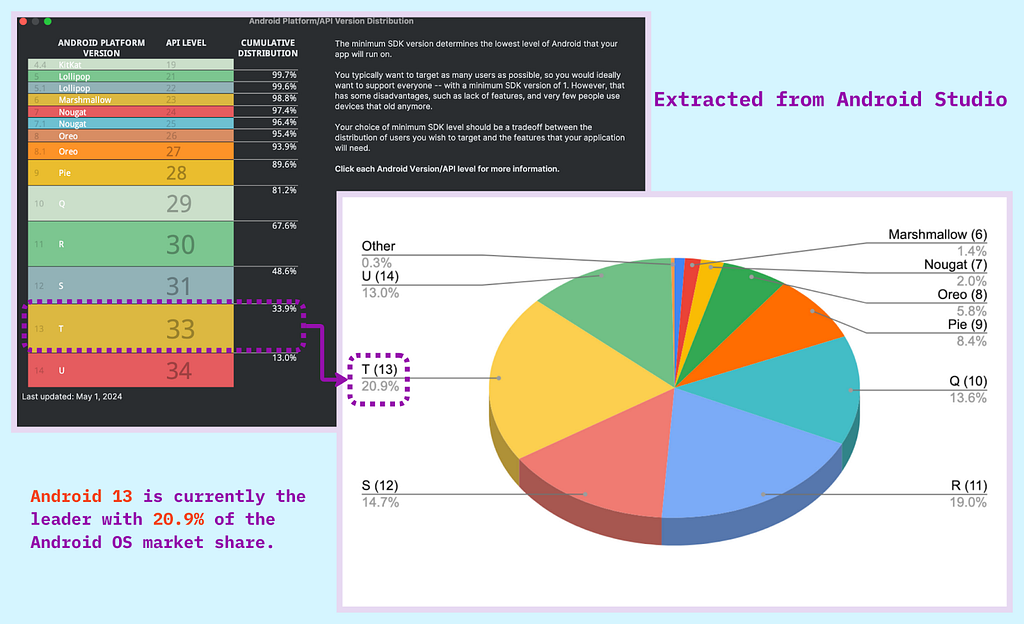
Hardware Diversity
The mobile market includes devices with a wide range of hardware specifications. This includes variations in processors, RAM, storage capacities, battery sizes, camera capabilities, and sensors. For example, high-end smartphones may feature powerful processors and large amounts of RAM, while budget models might have limited resources. This disparity necessitates careful optimization and testing to ensure that applications perform smoothly across all targeted devices (both high-end and low-end).

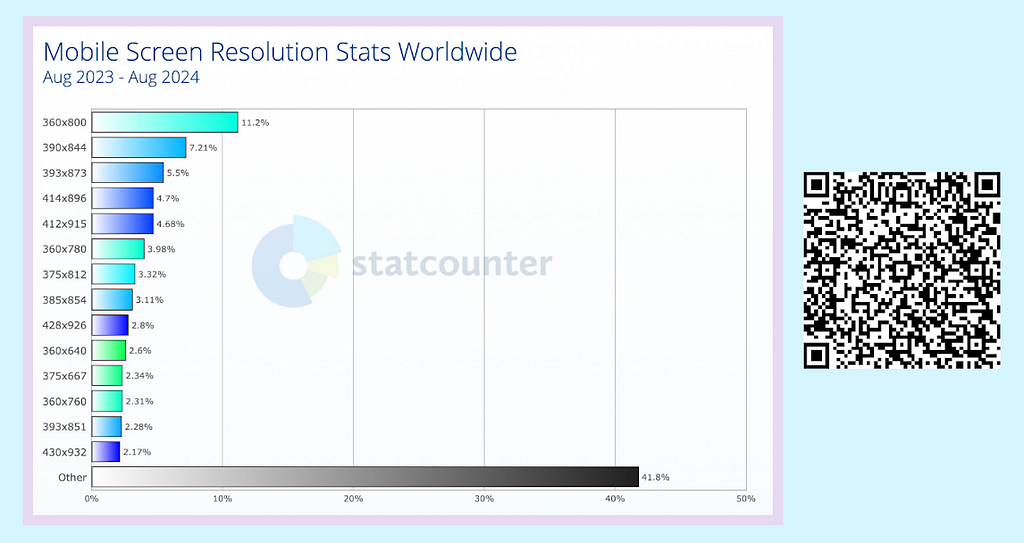
Screen Sizes and Resolutions

The diversity in screen sizes and resolutions further complicates the development process. Smartphones, tablets, and increasingly, foldable devices, offer a variety of display sizes and aspect ratios. Developers must design applications that adapt to different screen dimensions and pixel densities to provide a consistent and engaging user experience. This includes adjusting UI elements, graphics, and text to maintain usability and aesthetic appeal across devices.
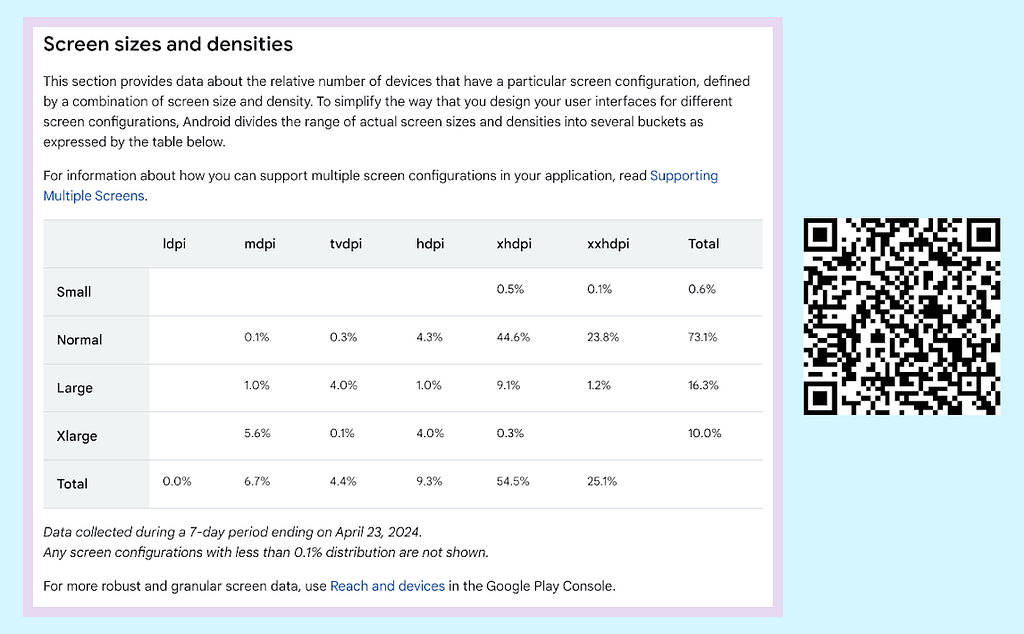
Google’s Material Design blog provides useful instructions on how to calculate device metrics, such as screen sizes, resolutions and other dimensions. Once device metrics are known, consult Android Distribution Dashboard for distribution data of screen sizes and densities.
Manufacturer Customizations
Many device manufacturers add custom layers and features on top of the base operating system, particularly in the Android ecosystem. These customizations can include unique UI elements, pre-installed applications, and modified system behaviors. Such alterations can lead to inconsistencies in how applications function across different devices, complicating development and testing processes.
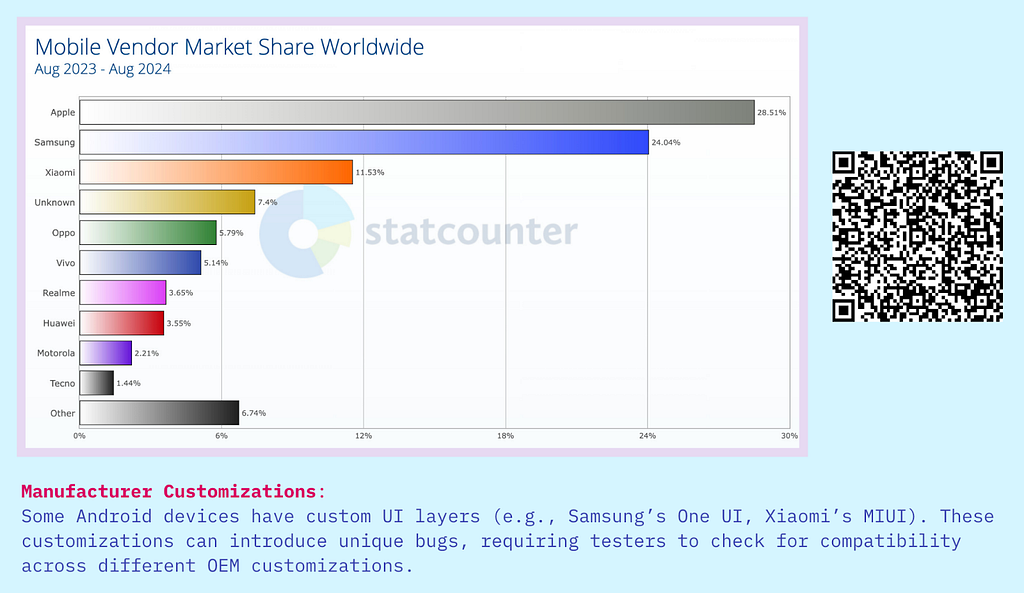
Implications of Mobile Device Fragmentation
Development Challenges
Developers must navigate a complex landscape when building applications for fragmented ecosystems. This includes ensuring compatibility with multiple OS versions, accommodating diverse hardware capabilities, and designing adaptive user interfaces. Moreover, they must implement fallbacks or alternative features for devices lacking certain hardware or software capabilities. For instance, an app relying on advanced camera APIs must offer basic functionalities for devices with simpler camera setups.
Testing Complexities

Testing across a fragmented device landscape is a monumental task. It is practically impossible to test an application on every conceivable device configuration. However, thorough testing is crucial to identify and fix bugs, optimize performance, and ensure a consistent user experience. This requires a strategic selection of test devices that represent a broad spectrum of the market, including different OS versions, hardware configurations, and screen sizes.

Performance Optimization
Optimizing applications for performance across diverse devices is challenging. An app that runs smoothly on a high-end device may experience lag or crashes on a device with lower specifications. Developers must optimize resource usage, including memory and CPU, to ensure that their applications are responsive and efficient on all target devices. This includes efficient coding practices, asset optimization, and careful management of background processes.
User Experience Consistency
Maintaining a consistent user experience across a fragmented device landscape is challenging. Differences in screen sizes, resolutions, and aspect ratios can lead to inconsistencies in how content is displayed. Developers must use responsive design techniques and scalable assets to adapt to different screen characteristics. Additionally, they must account for differences in input methods, such as touchscreens with varying sensitivities or devices with physical keyboards.
Strategies for Managing Mobile Device Fragmentation
Given the challenges posed by mobile fragmentation, software testers must employ a range of strategies to ensure comprehensive testing coverage. Here are ten effective ways to tackle mobile fragmentation:
1. Prioritize Devices and Platforms
The first step in addressing mobile fragmentation is to prioritize the key devices and platforms that are most relevant to your target audience. This involves analyzing market data to identify the most popular devices and OS versions used by your users. By focusing on these key devices and platforms, testers can ensure that the app performs well for the majority of users.
For example, if the target audience predominantly uses mid-range Android devices running versions 11 and 12, these configurations should be prioritized in testing. Similarly, testing on the latest iOS versions is essential if a significant portion of the user base is on Apple devices.
2. Use Real Devices for Testing
While emulators and simulators are valuable for initial testing, real device testing is essential to accurately assess how an app behaves in real-world conditions. Real devices provide insights into performance, battery usage, and hardware-specific issues that emulators might not fully capture. For example, an app’s interaction with physical sensors, such as GPS or accelerometers, can only be reliably tested on actual devices.
Maintaining a lab of real devices can be costly, but it’s a crucial investment for ensuring that the app functions well across the diverse range of devices in the market.
3. Leverage Cloud-Based Testing Platforms
To complement physical device testing, testers can utilize cloud-based testing platforms like BrowserStack, AWS Device Farm, or SauceLabs. These platforms offer access to a wide variety of devices and OS versions, enabling testers to conduct extensive testing without the need for an extensive physical device lab.
Cloud-based testing platforms also facilitate parallel testing, allowing multiple tests to run simultaneously on different devices, significantly speeding up the testing process.

4. Implement Cross-Platform Testing
Cross-platform testing is essential for ensuring that an app works consistently across both iOS and Android platforms. This involves running the app on multiple versions of each operating system to identify platform-specific bugs, performance issues, and inconsistencies in user experience.
Cross-platform testing tools like Appium and/or App Test Center can automate this process, making it easier to ensure broad compatibility without duplicating testing efforts.
5. Conduct Responsive and Adaptive Design and Testing

Mobile devices vary widely in terms of screen sizes and resolutions, from small smartphones to large tablets. To ensure a consistent user experience across all devices, testers need to conduct responsive and adaptive testing. This involves verifying that the app’s user interface adapts correctly to different screen sizes, orientations, and resolutions.
Testing tools, such as browser Responsive Design Mode and Appium WebDriver, can help automate the process, allowing testers to simulate various screen sizes and resolutions and identify potential UI issues.
6. Simulate Network Conditions
Mobile users access apps under a wide range of network conditions, from high-speed Wi-Fi to fluctuating cellular connections. Simulating these network scenarios during testing is crucial to ensure that the app remains functional and responsive, regardless of the user’s connectivity situation.
Network simulation tools allow testers to replicate different connectivity environments, such as 3G, 4G, 5G, or even offline conditions, helping to ensure that the app provides a seamless user experience in all scenarios.
7. Test Across Multiple OS Versions
Testing only on the latest OS versions is insufficient, as many users continue to operate on older versions. Ensuring compatibility with a range of OS versions, particularly those still in widespread use, is essential to avoid alienating a significant portion of the user base.
For example, while Android 13 might be the latest version, a significant number of users might still be on Android 11 or 12. Similarly, while iOS users tend to update quickly, there are often significant numbers using older versions like iOS 16. Comprehensive testing should cover these versions to ensure compatibility.
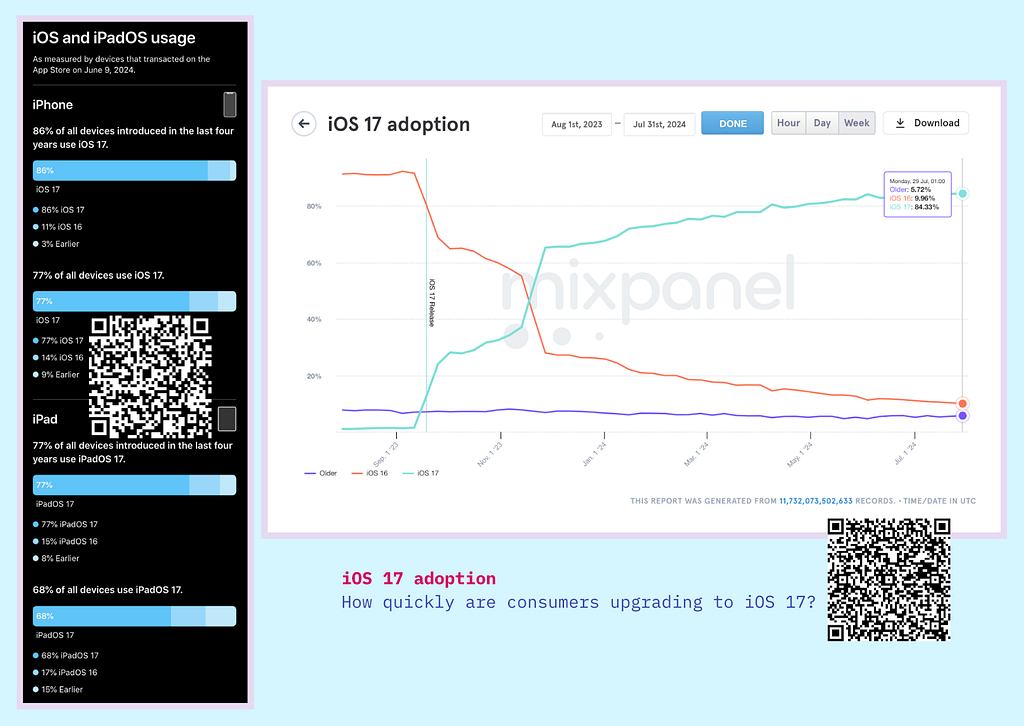
8. Continuous Integration and Automated Testing
Continuous integration (CI) and automated testing are critical in managing the complexities of mobile device fragmentation. By integrating automated tests into the CI pipeline, developers can quickly identify and address issues across different devices and OS versions. Automated testing can include unit tests, UI tests, and performance tests, providing a comprehensive approach to ensuring application quality.

9. Monitor and Analyze Post-Launch Feedback
Even with thorough pre-release testing, fragmentation-related issues can still arise after the app is released. Monitoring user feedback, crash reports, and usage analytics is essential for identifying these issues early and addressing them promptly.
Tools like Firebase Crashlytics or Sentry can help track crashes and errors, while user feedback channels provide insights into how the app performs on different devices and under various conditions. This continuous monitoring helps improve the app’s stability and performance over time.

10. Focus on Performance Testing
Performance testing is critical to ensuring that the app runs smoothly on devices with varying hardware capabilities. This includes testing for load times, memory usage, CPU utilization, and battery consumption. Performance testing tools like JMeter, LoadRunner, or Google’s Firebase Performance Monitoring can help assess how the app behaves under different loads and stress conditions.
By focusing on performance, testers can identify and address issues that could lead to poor user experiences, such as slow loading times or excessive battery drain, particularly on lower-end devices.
Conclusion
Mobile fragmentation presents significant challenges for software testers, but with a strategic approach, these challenges can be effectively managed. By prioritizing key devices and platforms, leveraging real and cloud-based testing environments, and implementing comprehensive testing strategies, testers can ensure that their app delivers a consistent and high-quality experience across the fragmented mobile landscape.
In today’s competitive mobile market, where user expectations are high and patience is limited, addressing mobile fragmentation is not just a best practice — it’s essential for the success of any mobile application. Through diligent testing, continuous monitoring, and a proactive approach to addressing fragmentation, testers can contribute to the delivery of robust, user-friendly apps that meet the needs of a diverse and growing user base.
References
- Market share of mobile operating systems worldwide from 2009 to 2024, by quarter: https://www.statista.com/statistics/272698/global-market-share-held-by-mobile-operating-systems-since-2009/
- As Mobile Screen Size Increases… So Does Activity: https://www.lukew.com/ff/entry.asp?1956
- StatCounter GlobalStats, Mobile Screen Resolution Stats Worldwide Aug 2023 — Aug 2024: https://gs.statcounter.com/screen-resolution-stats/mobile/worldwide/#monthly-202308-202408-bar
- How to Find Device Metrics for Any Screen: https://m3.material.io/blog/device-metrics
- Distribution dashboard: https://developer.android.com/about/dashboards
- StatCounter GlobalStats, Mobile Vendor Market Share Worldwide Aug 2023 — Aug 2024: https://gs.statcounter.com/vendor-market-share/mobile/worldwide/#monthly-202308-202408-bar
- Deciding What to Test: https://medium.com/@begunova/deciding-what-to-test-e42c51b444a9
- Responsive web design basics: https://web.dev/articles/responsive-web-design-basics
- W3C CSS Flexible Box Layout Module:https://www.w3.org/TR/css-flexbox/
- Emulator vs Simulator vs Real Device: https://medium.com/@begunova/emulator-vs-simulator-vs-real-device-15ce1dd5babf
- What is Cloud Testing (Example, Benefits & Best Practices): https://www.browserstack.com/guide/what-is-cloud-testing
- Appium Documentation: https://appium.io/docs/en/2.0/
- App Center Test: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/appcenter/test-cloud/
- Responsive Design Mode: https://firefox-source-docs.mozilla.org/devtools-user/responsive_design_mode/
- Mobile App Testing Checklist: https://github.com/lana-20/i_sliced_up_fun-SQA-mnemonic
- Mobile devices have been evolving, along with the respective cellular networks, bandwidths and protocols: https://github.com/lana-20/mobile-network-generations
- iOS and iPadOS usage: https://developer.apple.com/support/app-store/
- iOS 17 adoption: https://mixpanel.com/trends/#report/ios_17/from_date:-380,report_unit:week,to_date:-15
- Firebase Crashlytics: https://firebase.google.com/docs/crashlytics
- Mastering Performance Testing: a comprehensive guide to optimizing application efficiency: https://www.headspin.io/blog/a-performance-testing-guide
- JMeter User’s Manual: https://jmeter.apache.org/usermanual/index.html

𝓗𝒶𝓅𝓅𝓎 𝓉𝓮𝓈𝓉𝒾𝓃𝓰 𝒶𝓃𝒹 𝒹𝓮𝒷𝓊𝓰𝓰𝒾𝓃𝓰!
I welcome any comments and contributions to the subject. Connect with me on LinkedIn, X , GitHub, or Insta. Check out my website.
If you find this post useful, please consider buying me a coffee.
