
Monitoring HTTPS Network Traffic from APK with HTTP Toolkit, APK-MITM and Android Studio Emulator

Introduction
For Software Test Engineers, monitoring network traffic is crucial for debugging and ensuring that applications communicate as expected. However, HTTPS traffic on Adndroid poses a challenge due to its encrypted nature. This article introduces APK-MITM, a tool that simplifies the process of monitoring HTTPS traffic in Android applications. By patching APK file with APK-MITM, Sofware Test Engineers can easily inspect network traffic with the HTTP Toolkit and Android Studio Emulator for testing purposes.
What is APK-MITM?
APK-MITM (APK Man-in-the-Middle) is a tool designed to automatically modify Android APK files to allow network traffic interception. It simplifies the process of adding the necessary security configurations to the APK so that the HTTPS traffic can be intercepted and inspected using tools like HTTP Toolkit.
Prerequisites
Before getting started, ensure you have the following tools installed:
Setting Up APK-MITM
1. Install APK-MITM
First, install APK-MITM globally using npm:
npm install -g apk-mitm
2. Installing Java with Homebrew
Open Terminal
Open your terminal on your Mac.
Install Homebrew
If you haven’t installed Homebrew yet, you can install it by running the following command in your terminal:
/bin/bash -c "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Homebrew/install/HEAD/install.sh)"
Install Java
Once Homebrew is installed, use it to install OpenJDK:
brew install openjdk
Verify Installation
To verify that Java has been installed correctly, run:
java -version
Adding Java to the PATH
Add Java to PATH
Add Java to your PATH by appending the following line to your .zshrc file:
echo 'export PATH="/opt/homebrew/opt/openjdk/bin:$PATH"' >> ~/.zshrc
Reload .zshrc
Apply the changes to your current terminal session by reloading the .zshrc file:
source ~/.zshrc
Verify PATH Configuration
To confirm that the PATH has been updated correctly, run:
echo $PATH
Ensure that /opt/homebrew/opt/openjdk/bin is listed in the output.
Full Instructions Summary
Here is the complete sequence of commands to install Java and set up the PATH:
# Install Homebrew (if not already installed)
/bin/bash -c "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Homebrew/install/HEAD/install.sh)"
# Install OpenJDK
brew install openjdk
# Add OpenJDK to PATH
echo 'export PATH="/opt/homebrew/opt/openjdk/bin:$PATH"' >> ~/.zshrc
# Reload .zshrc to apply the changes
source ~/.zshrc
# Verify Java installation
java -version
# Verify PATH configuration
echo $PATH
Following these steps will ensure Java is installed and properly configured on your system, enabling you to use APK-MITM without any issues.
3. Prepare Your APK
Download the APK file of the application you want to test. Ensure that it is the exact version that you intend to monitor.
4. Patch the APK
Use APK-MITM to patch the APK for network interception:
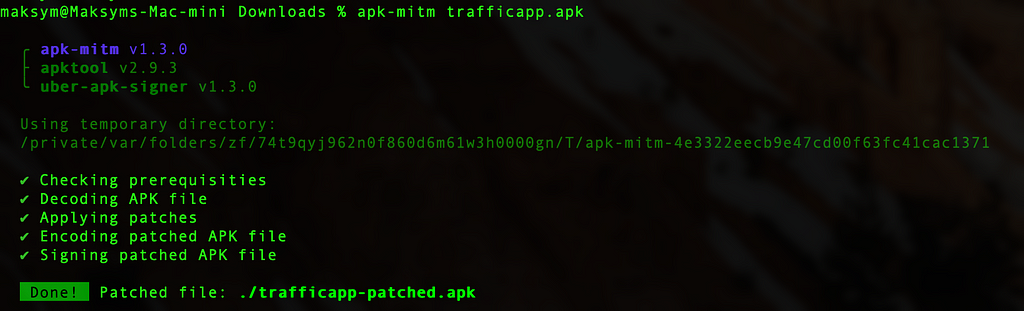
apk-mitm path/to/your/app.apk
This command will create a patched version of the APK in the same directory. You cab see the tool execution log in the Terminal.
Setting Up the Android Studio Emulator
-
Launch Android Studio
Open Android Studio and launch the Android Virtual Device (AVD) Manager. -
Create or Select an Emulator
Create a new emulator or select an existing one. Ensure the emulator is running. -
Install the Patched APK
Install the patched APK onto the emulator with the following command ot simply drag the file to the emulator from Finder.
adb install path/to/your/patched-app.apk
Configuring HTTP Toolkit
-
Launch HTTP Toolkit
Open HTTP Toolkit on your computer. -
Set Up Android Device
In HTTP Toolkit, select the option to intercept HTTPS traffic from an Android emulator. Follow the on-screen instructions to configure the emulator to trust the HTTP Toolkit’s certificate. This often involves installing the certificate manually on the emulator. -
Start Monitoring
Once the setup is complete, start monitoring the traffic. Open the application on the emulator and perform actions that generate network requests. You should see the traffic appearing in HTTP Toolkit.
Monitoring HTTPS Traffic
With the setup complete, you can now inspect the HTTPS traffic generated by the application. HTTP Toolkit allows you to view request and response headers, bodies, and other details, making it easier to debug network issues and verify that data is being transmitted correctly.
Conclusion
Using APK-MITM with the Android Studio Emulator and HTTP Toolkit streamlines the process of monitoring HTTPS traffic for QA Engineers. This setup not only simplifies the interception process but also provides a powerful way to inspect and debug network communications in your applications.
By following these steps, you can gain valuable insights into your application’s network behavior and ensure it meets the necessary standards for security and performance.
