
7 Stack Solutions in Python
Published on April 3, 2024
QA/SDET/SWE Stack Interview Questions —7 LeetCode Solutions
Let’s solve some coding problems related to the stack data structure.

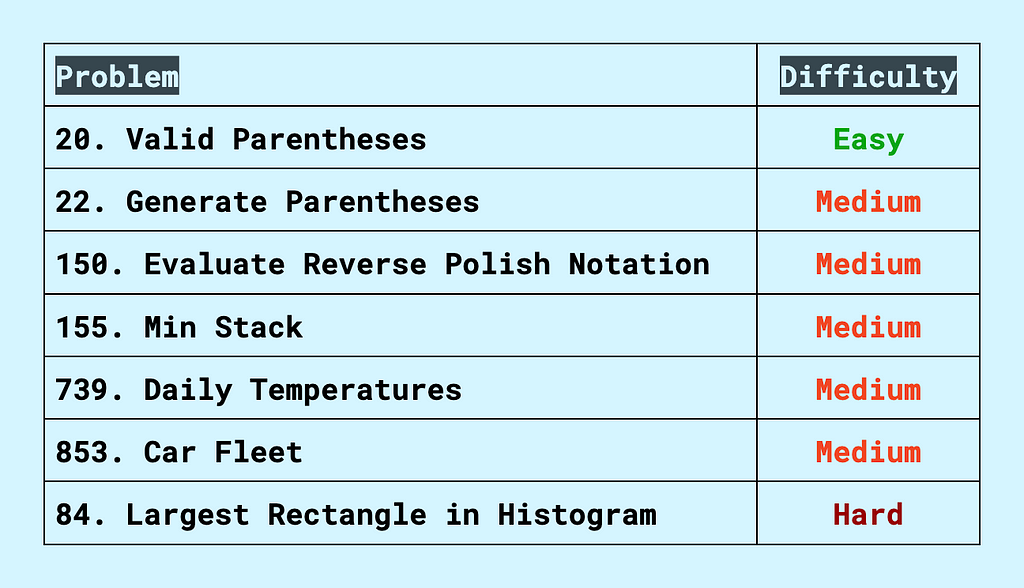
20. Valid Parentheses

Solution
class Solution:
def isValid(self, s: str) -> bool:
stack = []
closeToOpen = {")" : "(", "]" : "[", "}" : "{"}
for c in s:
if c in closeToOpen:
if stack and stack[-1] == closeToOpen[c]:
stack.pop()
else:
return False
else:
stack.append(c)
return True if not stack else False
# Test the function:
solution = Solution()
print(solution.isValid("()"))
print(solution.isValid("()[]{}"))
print(solution.isValid("(]"))
# Time: O(n) - we only go through every input character once.
# Space: O(n) - we use a stack, which can be up to the size of the input, which is n.
22. Generate Parentheses

Solution
class Solution(object):
def generateParenthesis(self, n: int) -> List[str]:
stack = []
res = []
def backtrack(openN, closedN):
if openN == closedN == n:
res.append("".join(stack))
return
if openN < n:
stack.append("(")
backtrack(openN + 1, closedN)
stack.pop()
if closedN < openN:
stack.append(")")
backtrack(openN, closedN + 1)
stack.pop()
backtrack(0, 0)
return res
# Test the function:
solution = Solution()
print(solution.generateParenthesis(3))
print(solution.generateParenthesis(1))
# Time: O((4^n)/sqrt(n)) - https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Catalan_number
# Space: O(n) - max depth of the recursive call stack is 2n, which is n.
150. Evaluate Reverse Polish Notation

RPN: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Reverse_Polish_notation
Solution
class Soluption:
def evalRPN(self, tokens: List[str]) -> int:
stack = []
for c in tokens:
if c == "+":
stack.append(stack.pop() + stack.pop())
elif c == "-":
a, b = stack.pop(), stack.pop()
stack.append(b - a)
elif c == "*":
stack.append(stack.pop() * stack.pop())
elif c == "/":
a, b = stack.pop(), stack.pop()
stack.append(int(b / a))
else:
stack.append(int(c))
return stack[0]
# Test the function:
solution = Solution()
print(solution.evalRPN(["2","1","+","3","*"])
print(solution.evalRPN(["4","13","5","/","+"])
print(solution.evalRPN(["10","6","9","3","+","-11","*","/","*","17","+","5","+"])
# Time: O(n) - we read through the input string, adding each value to the stack, and removing it at most once each (2n = n).
# Space: O(n) - we use a stack DS.
155. Min Stack

Solution
class MinStack:
def __init__(self):
self.stack = []
self.minStack = []
def push(self, val: int) -> None:
self.stack.append(val)
val = min(val, self.minStack[-1] if self.minStack else val)
self.minStack.append(val)
def pop(self) -> None:
self.stack.pop()
self.minStack.pop()
def top(self) -> int:
return self.stack[-1]
def getMin(self) -> int:
return self.minStack[-1]
# MinStack object is instantiated and called as such:
# solution = MinStack()
# solution.push(val)
# solution.pop()
# top = solution.top()
# min = solution.getMin()
739. Daily Temperatures

Solution
class Solution:
def dailyTemperatures(self, temperatures: List[int]) -> List[int]:
res = [0] * len(temperatures)
stack = [] # pair: [temp, idx]
for i, t in enumerate(temperatures):
while stack and t > stack[-1][0]:
stack_t, stack_idx= stack.pop()
res[stack_idx] = (i - stack_idx)
stack.append([t, i])
return res
# Test the function:
solution = Solution()
print(solution.dailyTemperatures([73,74,75,71,69,72,76,73])
print(solution.dailyTemperatures([30,40,50,60])
print(solution.dailyTemperatures([30,60,90])
# Time: O(n) - in the worst case, every element is pushed and popped once. This gives a time complexity of O(2n) = O(n).
# Space: O(n) - monotonic stack - stack grows to a size of n elements at the end.
853. Car Fleet

Solution
class Solution:
def carFleet(self, target: int, position: List[int], speed: List[int]) -> int:
pair = [[p, s] for p, s in zip(position, speed)]
stack = []
for p, s in sorted(pair)[::-1]: # reverse sorted order
stack.append((target - p) / s)
if len(stack) >= 2 and stack[-1] <= stack[-2]:
stack.pop()
return len(stack)
# Test the function:
solution = Solution()
print(solution.carFleet(12, [10,8,0,5,3], [2,4,1,1,3])
print(solution.carFleet(10, [3], [3])
print(solution.carFleet(100, [0,2,4], [4,2,1])
# Time: O(nlogn) - sort input based on the position
# Space: O(n) - using a stack
84. Largest Rectangle in Histogram
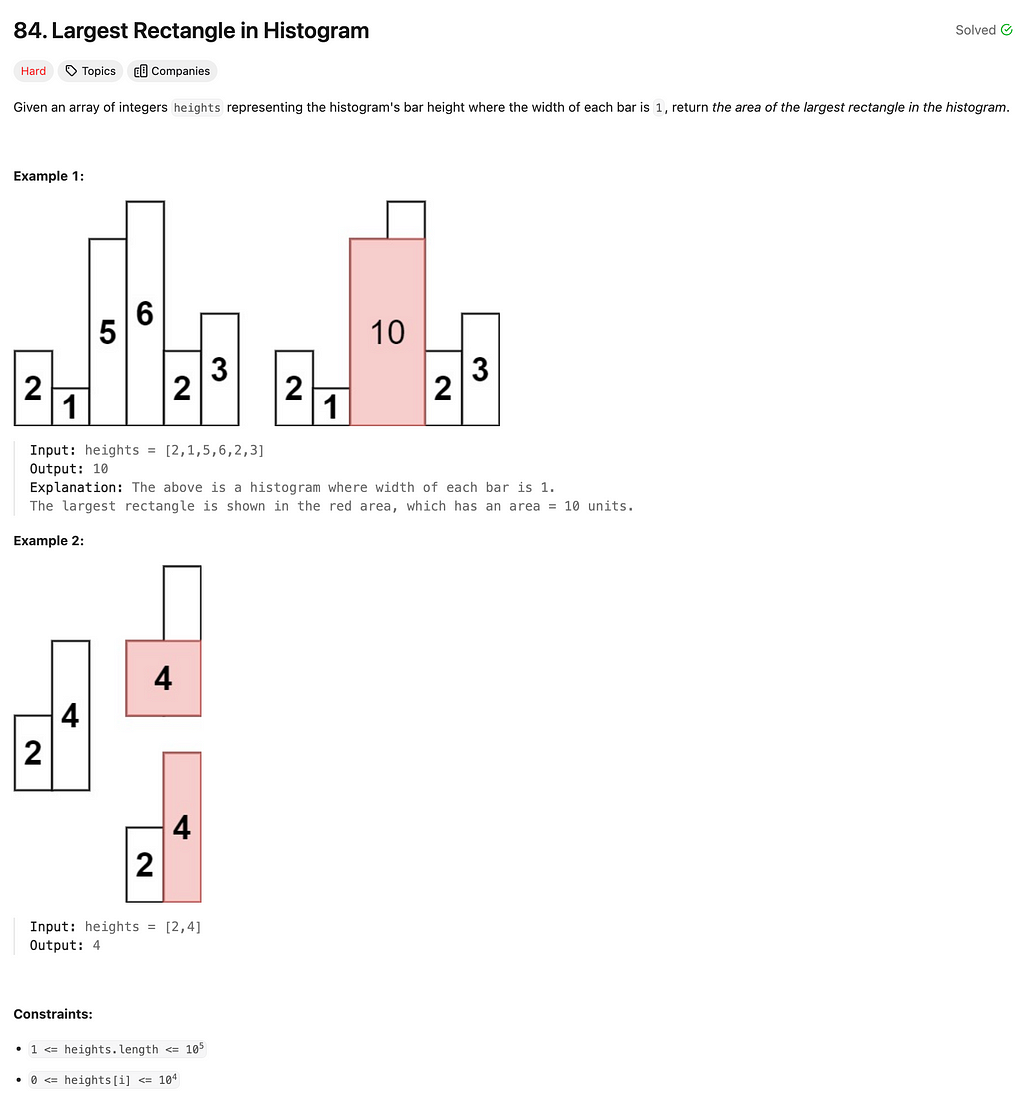
Solution
class Solution:
def largestRectangleArea(self, heights: List[int]) -> int:
max_area = 0
stack = [] # pair: (index, height)
for i, h in enumerate(heights):
start = i
while stack and stack[-1][1] > h:
index, height = stack.pop()
max_area = max(max_area, height * (i - index))
start = index
stack.append((start, h))
for i, h in stack:
max_area = max(max_area, h * (len(heights) - i))
return max_area
# Test the function:
solution = Solution()
print(solution.largestRectangleArea([2,1,5,6,2,3])
print(solution.largestRectangleArea([2,4])
# Time: O(n)
# Space: O(n)

Hope you find these solutions helpful. If you do, please make sure to follow me on LinkedIn, X , GitHub, or IG.
If you find this post useful, please consider buying me a coffee.
